Authors: Rajendra Jangid and Mahendra
Department of Agricultural Economics, S.K.N. Agriculture University
Jobner-303329, Jaipur, Rajasthan, India
*Email: rajendra94jangid@gmail.com
Introduction
- 80% of Rajasthan’s population resides in rural area
- Sector contribution to the state GDP is around 22.5%
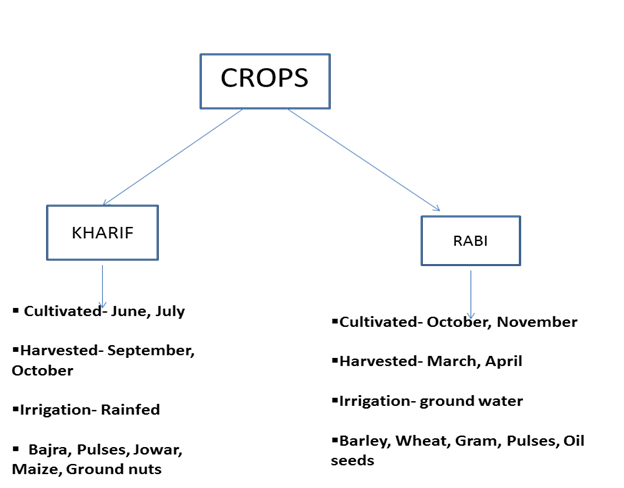
- Cultivated area of 20 million hectares but only 20% of the total cultivated area is irrigated
- Farmers depend largely on both rainfed and ground water agriculture
- This has led to a decrease of ground water level.
| CROPS | NAME OF PRODUCING DISTRICTS |
| Jowar | Ajmer, Pali, Tonk, Nagaur, Bharatpur, Alwar, Jodhpur, Bhilwara, Kota. |
| Bajra | Barmer, Jodhpur, Nagaur, Churu, Jhalore, Sikar, Jhunjhunu, Jaipur, Alwar |
| Wheat | Ganganagar, Jaipur, Alwar, Bharatpur, Kota, Bundi, Hanumangarh, Chittor. |
| Barley | Jaipur, Sikar, Alwar, Ganganagar, Hanumangarh, Nagaur, Bhilwara, Ajmer, Dausa. |
| Gram | Churu, Hanumangarh, Jaipur, Ajmer, Sikar, Jhunjhunu, Alwar, Tonk. |
| Moong | Nagaur, Jaipur, Jodhpur, Sikar, Jalore, Jhunjhunu, Almer. Barmer, Tonk. |
| Urad | Chittore, Banswara, Udaipur, Dungarpur,Jhalwar, Bhilwara |
The National Commission on Agriculture defined agricultural marketing as a process which starts with a decision to produce a saleable farm commodity and it involves all aspects of market structure of system, both functional and institutional, based on technical and economic considerations and includes pre and post- harvest operations, assembling, grading, storage, transportation and distribution.
GOVERNMENT INSTITUTIONS:
- Commission of Agriculture Cost and Prices
- Food Corporation of India
- Cotton Corporation of India
- Jute Corporation of India
INITIATIVES TAKEN BY THE GOVERNMENT OF RAJASTHAN - Gloden Rays Project
- Weather Based Crop Insurance
- Promotion of Organic Farming
- Research and Education
- Promotiom of Olive cultivation
STRATEGY
Some of the state’s effective agro marketing strategies are
Amendments to the APMC Act: In Rajasthan, reforms to APMC Act have been done for Direct Marketing and Contract farming.
Direct marketing: License for Direct Marketing has been granted in Rajasthan to ITC e-choupal.
Contract Farming: Helps in increasing the income of the farmers.
Development of mega markets
MARKET SUPPORT
- Under MIS garlic production increased significantly in 2011-12
- Procurement under MIS during 2012-13 was hardly 62799 quintals
- Procurement was made at the rate of 1700 rupees per quintal
- Prices were very low during 2012-13
- Government suffered huge loss due to this procurement There was significant decrease in gram production under PSS in 2011-12 as compared to earlier year 2010-11.
INFRASTRUCTURE
- There are only 22 rural godwons in the state as compared to 310 in Andhra Pradesh and 334 un Bihar
- Has 209 grading labs which which is much moire than 44 in Andhra Pradesh and 62 in Punjab
- Cooperatives in the state if of area 342, 236 sq km
- Need to construct more scientific storage facility in the rural area
- Private sector involvement is also necessary as huge capital is needed for storage infrastructure.
CONCLUSION
Issues that need to be addressed for the benefit of the farmers:
- Assurance of remunerative price for their produce
- Timely payment of their sale proceeds , no commission charges from the farmers
- Adequate storage facilities for farm produce
- Mandis at nearby places
- Proper and timely transportation facility
- Widening reach of contract farming and direct marketing
- Provide facilities for export purpose
About Author / Additional Info:
I am currently pursuing Ph.D. in Agricultural Economics from SKRAU, Bikaner.