Author: Vora Zarna N.
Ph.D. (Scholar), Department of Genetics and Plant Breeding, Junagadh Agricultural University, Junagadh, Gujarat, India.
Correspondence email id: zarna2893@gmail.com
Introduction
Accumulation of desirable alleles in a population through various breeding techniques is known as population improvement and those breeding procedures that are used for such work are referred to as population improvement approaches. In plant breeding, following four approaches are used for population improvement.
- Recurrent selection
- Disruptive
- Diallel selective mating, and
- Biparental mating
- Recurrent selection Recurrent selection refers to reselection generation after generation with intermating of selects to provide for genetic recombination. It is an important method of improving the frequency of desirable alleles in a plant breeding population. This method was originally developed for genetic improvement of cross pollinated species, Now it is also used for population improvement in self pollinated species.
- Disruptive selection This is another breeding technique which is used for development of superior genotypes in a population. In this breeding approach, both extreme types for a character are selected in the segregating population and intermating is done among selected plants. Suppose we want to develop early maturing genotypes. To achieve this goal, plants with extreme earliness and lateners are selected in F 2 or later generations of a cross and mating is done between early and late plants. Several selection and mating and selection was developed by Mather (1953) and Thoday (1958, 1960).
Features:
- This method is applicable to the genetic improvement of both self and cross pollinated species.
- Disruptive selection may be considered a form of recurrent selection because this method also involves selection and intermating of superior plants in segregating population.
- It differes from the directional selection.
Merits:
- Disruptive selection is an efficient breeding method for breaking undesirable linkages, releasing genetic variability, generating diversity and improving the adaptation of plant populations.
- Disruptive selection is useful when wild germplasm is utilized in the breeding programmes. It will break repulsion phase linkages in such breeding programmes.
Demerits
- Repeated crosses have to be made for improvement of a particular character.
- Populations of limited crosses can be handled by this method at a time.
- Diallel selective mating design The concept of diallel selective mating system was originally developed by Jensen in 1970. Jensen used this system for genetic improvement of wheat. Now this system is used for genetic improvement of various autogamous crops especially small grain crops such as wheat, rice, etc.
Features
- This is an effective method of improving those autogamous species which are difficult to cross and have few seeds per cross. Thus, it is useful in improving small grain crops.
- This is an important method of population improvement in self pollinated species. Thus, it supplements conventional breeding methods in autogamous crops.
- This is generally considered as a form of recurrent selection, because it involves selection and intermating in segregating generations.
- Both mass and recurrent selection procedures are used for handling of materialin this system. Thus, it permits use of conventional breeding method as well as improvement of population by intermating.
- In this system, superior or promising genotypes can be identified and isolated for development of new cultivars at any stage of breeding programme.
- It also permits incorporation of new germplasm at any stage in the breeding programme.
- In the conventional breeding methods, usually two parents are included in the breeding programme at a time. This system permits inclusion of multiple parents in the breeding programme.
- This system fulfills both short term and long term breeding goals, because it permits use of conventional selection procedures at any stage in the breeding programme as well as broadens the genetic base of populations.
- The end product of this system can be used as a pureline variety, a mass selected variety or as a parental lines for further lines for further use in the breeding programme.
Merits :
- Useful in broadening the genetic base of populations by incorporation of multiple parents in the breeding programme.
- This system is very effective in breaking undesirable linkage blocks, because it permits intermating of selected plants in segregating generations. It fasters the genetic recombination.
- This system also results in creation of vast genetic variability for various economic characters. This is possible due to incorporation of multiple parents in the breeding programme and intermating in segregating populations.
- In small grain crops, this system has been reported to be very effective in delaying new cultivars.
Demerits:
- Large number of crosses have to be made to obtain sufficient quantity of crossed seeds. This is a difficult task without the use of male sterility.
- It involves handeling of materials by mass selection as well as intermating in segregating populations which requires more labour and space.
- This method is less effective in improving those characters which have low heritability.
- This system is rarely used in crop improvement and has not become very popular so far.
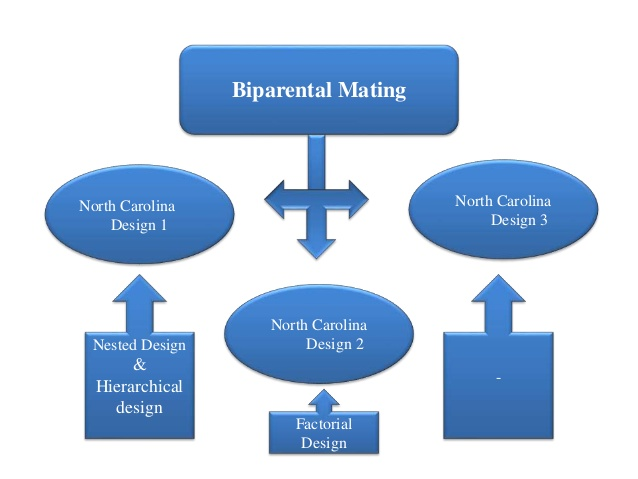
It refers to crossing among randomly selected plants in F2 or subsequent generations of a cross in a definite fashion. The concept of biparental mating was originally developed by Comstock and Robinson.it is an important method of concentrating favourable genes in population. Three or four cycles of biparental mating are required to achieve the desired improvement.
Merits :
- It is very effective in breaking undesirable linkages.
- This technique leads to creation of vast genetic variability in a population for various economic characters.
- This technique is applicable for genetic improvement of both self and cross pollinated species.
- This is an easy and effective method of population improvement.
ImageSource:https://www.google.co.in/search?q=biparental+mating&oq=biparental+&aqs=chrome.1.69i57j0l5.4272j0j7&sourceid=chrome&ie=UTF-8
Demerits :
- Large segregating population has to be grown for selection and intermating to achieve desired improvement.
- Repeated biparental mating has to be made for 3-4 generations.
- This technique permits handling of limited segregating population at a time.
- Essentials of Plant Breeding, By, P. singh (2004), Kalyani publishers, 169-173.
- Singh, B. D., Plant Breeding Principles and methods, (2012), Kalyani Publishers,7: 132-134.
About Author / Additional Info:
Pursuing Ph.D. Genetics and Plant Breeding at Junagadh Agricultural University, Junagadh.