Author: Deepti
Introduction
Human inventions made life very comfortable one such invention is synthetic plastic by Leo Hendrik Baekeland in 1907. Plastics are strong, light-weighted, durable and can be casted into any desired shapes and size on heating. These properties make plastic versatile in various fields of application like food, clothing, shelter, transportation, construction, medical and recreation industries. As the demand of plastic is increasing, production also increasing steadily.
The major disadvantage of plastic is the large-scale accumulation of plastics waste in the biosphere. These plastics waste do not decompose and remains for a long time, creating severe environmental and health issues. Scientists around the world are looking for eco-friendly techniques for the safe handling and management of the plastic waste, which can restore life and create a renewed environment.
What really happens after the use of plastic?
Trillions of plastics items are made each year, but after it's use it becomes a waste and remains in the environment without any deterioration lasting 1000 years. These plastic wastes are discarded in the landfill. When rain water flows through these waste, it absorbs the water-soluble compound and mix with highly toxic compound of plastic waste. This leads to Leachate, effecting the ground water, soil, stream, rivers and seas. All these in turn affects the human health severely.
Effect on marine life’s
The accumulation of plastics in the marine food chain is causing global concern. As demand for plastic material is increasing, its production and accumulation of waste is also increasing. These plastic from landfill go into streams, flows into rivers and ultimately reaches oceans. Where the ocean current traps the millions of plastics, forming enormous garbage gyres. Over one million marine life’s, and other birds and animals die each year from plastic trash. By seeing the colour of plastic waste they confuse it as food and feed on them. Nearly 700 species are at risk due to plastic entanglement, or ingestion, chocking, intestinal blockage, starvation etc. If we don’t think and act on it, our future generation will only see these birds, animals and marine life in books and google, like how sparrows extinct away from our site.
Human health is effected
Research proved that plastics destroys human health in many direct and indirect ways. Muthukumar and Veerappapillai, (2015) reported that phthalate are esters of phthalic acid which is mainly used as plasticizers. It migrates into the air to food and finally to people including babies in their mother’s wombs. Adverse outcomes, including increased adiposity and insulin resistance, decreased anogenital distance in male infants, decreased level of sex hormones and problem in human reproductive system both for males and females. Some other constituents of plastic such as benzene are known to cause cancer. The accumulation of plastic waste in marine life is steadily affecting the food chain (Biomagnification). The organic chemicals from plastic may transfer into lower tropic level organisms (e.g. Zooplankton) via ingestion and at much greater concentrations in higher trophic level organisms (e.g. small fish and sharks). This ultimately lead to contaminated seafood for humans.
Soil fertility is effected
Open dumping of waste in landfills, attract many flies and mosquitoes and it multiplies faster, leading to the spread of many diseases for example malaria, respiratory diseases, gastrointestinal diseases, vomiting, diarrhea, chest pains, cholera, irritation of the skin, nose and eyes etc.





An alternative for synthetic plastic: Biodegradable Bioplastic
Biodegradable Bioplastics are plastics that are decomposed by the action of microbes. Biodegradation process refers to the degradation and assimilation of polymers by living microorganisms to produce degradation products. The most important organisms in biodegradation are fungi, bacteria and algae.
Natural polymers example rubber, starch, cellulose, protein is biodegradable bioplastic, which on decomposition produces CO2. The liberated CO2 along with the water and sunlight can be used for the process of photosynthesis. So, the cycle continuous.
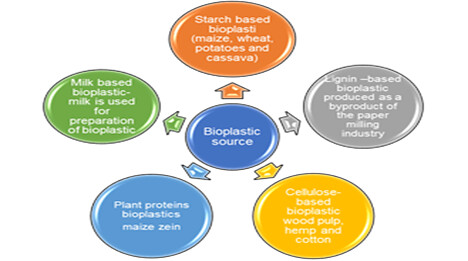
Fig No: 1.2 - The different source of Bioplastic
Edible starch based plastic from potato, cassava, corn starch etc. can be a best option for this synthetic plastic. Starch based biodegradable bio-plastics offer a lot of advantages such as:
- Non-toxic less accumulation of bulky plastic materials in the environment, as they can be decomposed easily.
- They are edible.
- Soil fertility is not effected.
- Minimize injuries to wild animals, marine life, if they eat these bio plastics it may act as a source of food only.
- Reduction in the cost of waste management.
- These all ultimately improves the human health and create a safe ecosystem.
Areas where we must give more focus:
Waste management-it is an important area to be focused as trillions of plastic items are made each year. Out of the whole production about 5% goes to recycling and 50% goes to land fill. The rest find its way into the environment which ultimately end up in sea forming enormous garbage gyres and enter the food chain. Following are the areas to be focused:
- It reduces the spread of diseases.
- to create a clean and healthy environment.
Key points to remember:
- Stop production of synthetic plastics and encourage starch based biodegradable bioplastics.
- The proper waste management and dumping of waste plastic into landfills should be stopped.
- Creating more industries for plastic waste management by assigning people for proper collection, washing, recycling, reuse or recreating it into any other useful product.
- Creating awareness among people about the plastic hazards and encouraging them to use biodegradable bio-plastics.
- Respect the people who work in these areas.
- While going for shopping prefer Eco bags, paper bags, card box, basket, jute bags etc. which are easily compostable.
- To clean up ocean is easy? or the way by which you can stop this trash or plastic waste not to reach the ocean is more easy? These can be done by proper waste management by not dumping in landfill or waterbodies.
References:
1. Muthukumar. A., and Veerappapillai. S. (2015) Biodegradation of Plastics - A brief review, International Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences., 31(2):204-209.
2. www.google.com
About Author / Additional Info:
I just finished my MTech in Industrial Microbiology (Biotechnology) from University of SHUATS, Allahabad.