Author: Anushree Pramanik
In recent years, agricultural production is facing serious challenges due to climate change. Therefore, the breeding of green crops based on agricultural genomics is becoming the key to solving these problems. Producing more high quality, safe food on less land with less environmental impact is one of the greatest challenges of the 21st century. The main aim of agricultural genomics is: Increase crop production, Enhance quality of products and to provide protection to the environment by maintaining a chain of sustainable works that conserves the ecological basis of plants, to take care of all such issues agriculture genomics is standing in form in front of researchers. Due to availability of traditional and high throughput sequencing platforms ,there are several milestones of genomics in agriculture ,availability of expressed sequence tags (EST), BAC end sequence, analysis of germplasm , genetic diversity analysis, mutant collections and expressions analysis, TILLING and Eco-TILLING. Advance genomics helps in identifying the segment of the genome responsible for adaptation, better understanding of natural selection and offer the potential to speed up with the promising agronomic traits. With the emerging advances and expansion of bioinformatics tools tremendous work has been done on various fields such as
(1) Comparative genomics
(2) Transcriptome analysis
(3) Functional genomics
(4) Metabolomics
(5) Genotyping and marker assisted breeding.
(6) Recombinant DNA technology.
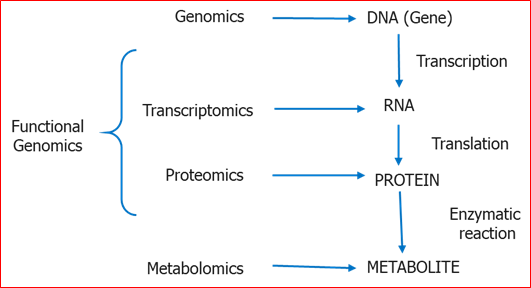
• Genome: Complete set of genetic information, including all of its genes found in each cell.It includes both nuclear and cytoplasmic gene
• Functional genomics: Determining the role of genes through gene disruption (knockouts, underexpression and overexpression)
• Comparative genomics: Comparison of one genome to another
• Proteome: The term proteome refers to the complete set of proteins produced in a cell during a specific developmental stage and under the given environmental conditions.
• Transcriptome: It is full complement of RNA molecules, including their quantities, produced by a cell during a specific developmental stage and exposed to a given environment.
• Omics: Refers to innovative technology platforms such as genomics, proteomics, Transcriptomics, metabolomics etc.
Application of Genomics:
• Improve the ideotype of crop plants to promote resistance to several biotic and abiotic factors such as pest, disease , floods drought, salinity etc.
• Help with the goal to grow more from less.
• Helps in the breeding of disease resistant, superior quality livestock for the production of healthy herd.
References:
• Wenqin Wang, Xuan H. Cao, Mihai Miclauș, Jianhong Xu, and Wenwei Xiong. The Promise of Agriculture Genomics. (2017) International Journal of Genomics. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/9743749
• B D Singh and A K Singh (2016) Marker Assisted Plant breeding: Principles and Practices ISBN 978-81-322-2315-3 ISBN 978-81-322-2316-0 (eBook) DOI 10.1007/978-81-322-2316-0.
About Author / Additional Info:
I am currently pursuing MSc in Genetics and Plant breeding from RVSKVV Gwalior.